- Academic Technology
How Teachers and Trainers Are Bringing Experiential Learning Into The Classroom with Video
For just about all of us, our day-to-day experiences are a constant — and important — source of new knowledge.
The intentional practice of experiential learning — a widely recognized high-impact learning method — offers a unique opportunity for both academic and professional students to gain a better understanding of a new concept by applying that learning to a real-world problem.
The benefits of experiential learning stem from its learner-centric approach that is both engaging and effective. Experiential learning bridges the gap between theory and practice, accelerates learning, and enables personalized learning through individual experiences.
In fact, learning through experiences is so valuable in some professions that many educational programs require students to complete experiential learning requirements such as internships, fellowships, clinicals, and student teaching in order to graduate.
But what if students had more access to experiential learning in the classroom? The impact on learning would be transformative.
Teachers and trainers alike have been hard at work finding new ways to harness the benefits of experiential learning without actually leaving the classroom. And one particular technology they’ve found that enables them to bring the real-world into the classroom is video.
Supporting Experiential Learning In The Classroom With Video
Planning and executing experiential learning exercises in the classroom can be difficult for a few reasons: time is limited, and fully immersing each student in real-world experiences at once can be tricky. But over the years, teachers and trainers have found creative ways to circumvent these challenges with the help of video.
The following are ways instructors are using video technologies to bring experiential learning into their classrooms.
Making Time for Experiential Learning Activities
Passive learning, through instructor-led presentations, has historically dominated class time, forcing possible experiential learning activities outside of the classroom. But as the number of instructors utilizing blended learning methods (most notably, flipped classroom strategies) continues to grow, so too is the class time available for experiential learning exercises.
Instructors with access to presentation recording software are taking advantage of video technology to record more and more digital course content that can be viewed online — and in doing so, freeing up time in-class time for other active and experience-based learning.
Recording Experiential Learning Activities For Reflection and Feedback
Presented with the challenge of making in-class experiential learning inclusive and impactful for all students, instructors have found inventive applications for video recording software that reinforces critical pieces of the experiential learning model (ELM) — instructor feedback to help conceptualize the experience, and reflective observation — for all students.
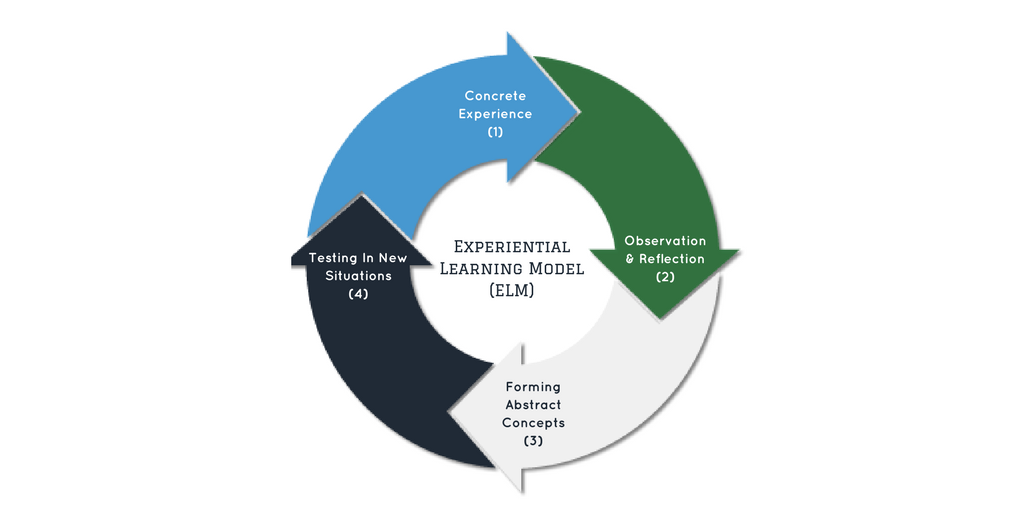
With smaller peer-to-peer breakout activities, such as one-on-one role play, the instructor can only provide limited feedback to students participating in experiential learning activities during class time. And with larger classroom simulations or projects that aim to involve all students in one group activity, for example a mock trial in a courtroom, not all students will have an equally immersive experience that will improve their understanding of the materials upon reflection.
Instructors are still facilitating similar small and large group experiential learning activities, but they are using video recording software to deepen the learning experience.
Examples of Video-Supported Experiential Learning Activities
MBA Students Practice Presentations Skills
At University of British Columbia’s Sauder School of Business, visionary leaders set out to design more courses that utilized experiential learning in order to arm MBA students with the presentation skills they would need in the workforce.
The Sauder School of Business found a creative solution to support experiential learning with Panopto’s presentation recording software. Instructors in the Business School used laptops loaded with Panopto to build a media lab containing dozens of student recording stations. Hundreds of students recorded presentations in just a few days that they were then able to use for personal reflection and submit for feedback from instructors.
Read more about how Sauder MBA students benefit from video on campus.
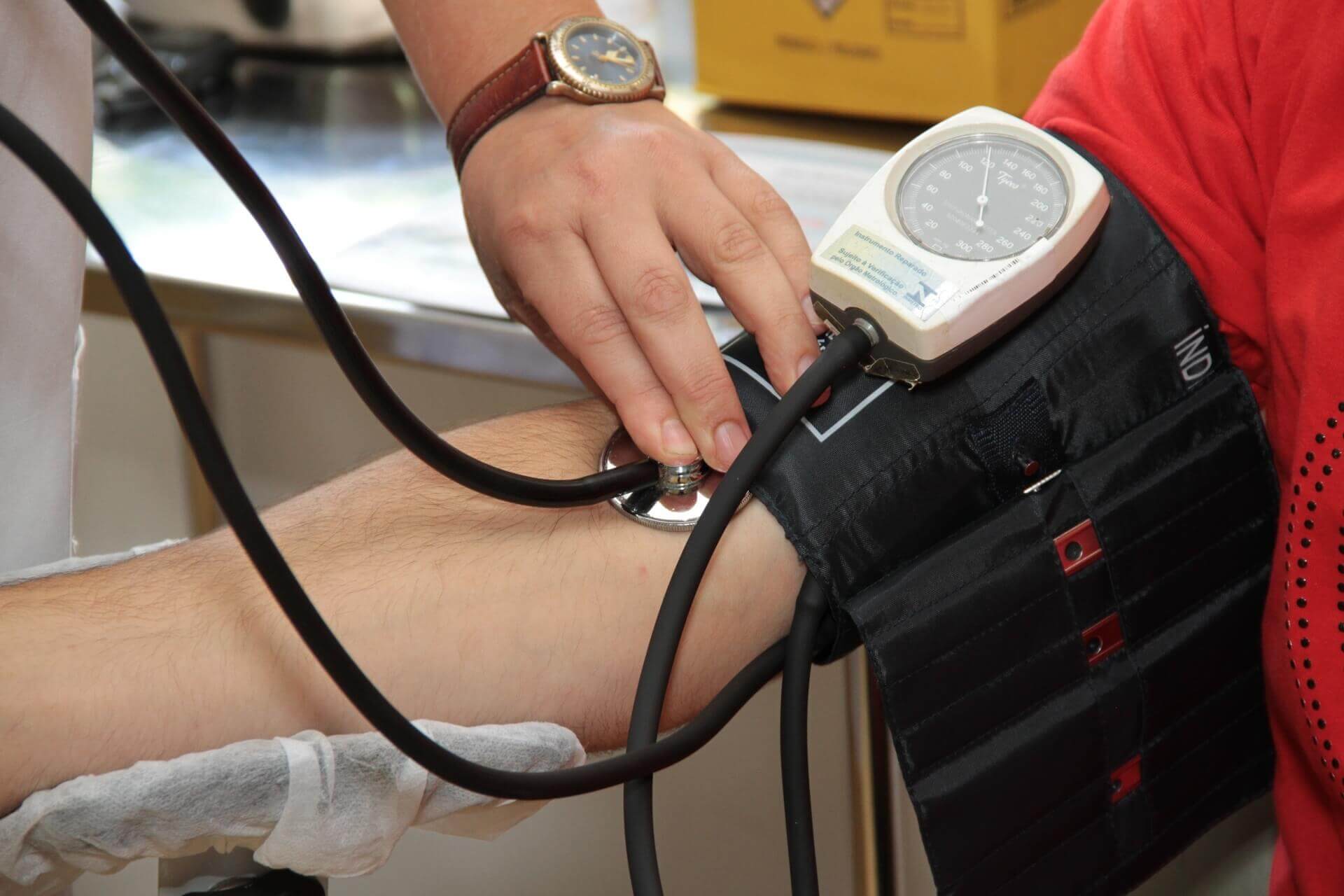
Medical Students Simulate Patient Interactions
The University of Butler began using iPads equipped with Panopto’s mobile app in order to create experiential learning opportunities on campus for Physician Assistant students. Students record themselves role-playing patient interactions, and then upload the videos to their school’s video content management system. Not only are Butler’s Physician Assistant students able to review and critique their own experiences, but their professors can view the videos at any time and leave insightful feedback for the students.
By recording the patient interactions, the students reap the full benefits of experiential learning without leaving campus. Not only do students at Butler internalize their learnings better, but they graduate with sharper skills that they can apply immediately on the job. Jennifer Snyder, Associate Professor in the Physician Assistant program at Butler adds, “Being able to record their practices gives them a feeling of comfort.”
Read how Butler uses student recordings and presentations.
Make Experiential Learning In Your Classroom Even More Powerful
Find out how Panopto’s video presentation software can help you improve learning for students — contact us for a free trial.